Discover What is Porosity in Welding and Its Impact on Structural Honesty
Discover What is Porosity in Welding and Its Impact on Structural Honesty
Blog Article
Recognizing Porosity in Welding: Exploring Reasons, Results, and Avoidance Techniques
As specialists in the welding market are well aware, comprehending the reasons, effects, and prevention strategies associated to porosity is crucial for accomplishing durable and trustworthy welds. By delving right into the root triggers of porosity, examining its destructive effects on weld high quality, and exploring effective avoidance methods, welders can boost their knowledge and skills to create premium welds regularly.
Typical Root Causes Of Porosity
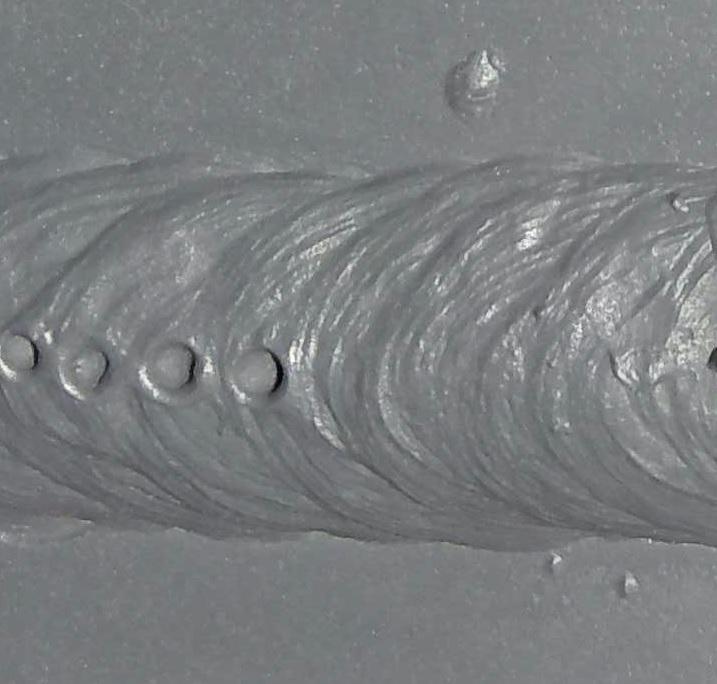
Porosity in welding is mainly brought on by a mix of variables such as contamination, inappropriate securing, and inadequate gas coverage during the welding procedure. Contamination, in the kind of dust, oil, or corrosion on the welding surface area, produces gas pockets when heated up, resulting in porosity in the weld. Inappropriate securing takes place when the securing gas, frequently made use of in processes like MIG and TIG welding, is incapable to totally shield the molten weld pool from responding with the bordering air, leading to gas entrapment and subsequent porosity. In addition, poor gas protection, typically because of incorrect circulation rates or nozzle positioning, can leave parts of the weld unprotected, permitting porosity to create. These variables collectively contribute to the development of voids within the weld, weakening its honesty and possibly triggering structural concerns. Recognizing and attending to these common reasons are important actions in protecting against porosity and ensuring the top quality and strength of welded joints.
Impacts on Weld Top Quality
The visibility of porosity in a weld can dramatically jeopardize the overall high quality and honesty of the bonded joint. Porosity within a weld creates gaps or tooth cavities that damage the structure, making it much more prone to splitting, corrosion, and mechanical failure. These voids function as stress concentrators, decreasing the load-bearing capacity of the weld and increasing the chance of premature failing under used stress. In addition, porosity can likewise act as prospective sites for hydrogen entrapment, additional worsening the destruction of the weld's mechanical properties.
In addition, porosity can hinder the effectiveness of non-destructive screening (NDT) methods, making it testing to identify various other problems or interruptions within the weld. This can cause substantial safety and security worries, particularly in crucial applications where the architectural honesty of the bonded elements is critical.
Prevention Techniques Review
Provided the detrimental influence of porosity on weld quality, effective avoidance techniques are critical to preserving the architectural stability of welded joints. Among the primary prevention strategies is detailed cleaning of the base products prior to welding. Pollutants such as oil, grease, rust, and wetness can contribute to porosity, so making certain Website a clean job surface area is necessary. Proper storage space of welding consumables in completely dry conditions is additionally essential to avoid wetness absorption, which can bring about gas entrapment during welding. In addition, selecting the proper welding criteria, such as voltage, current, and travel rate, can help lessen the threat of porosity development. Guaranteeing appropriate protecting gas flow and coverage is one more critical prevention method, as not enough gas insurance coverage can result in atmospheric contamination and porosity. Appropriate welder training and accreditation are necessary for implementing preventive steps efficiently and regularly. By incorporating these prevention methods into welding practices, the occurrence of porosity can be significantly reduced, resulting in stronger and more dependable welded joints.
Importance of Proper Protecting
Appropriate protecting in welding plays a crucial function in protecting against climatic contamination and making sure the stability of bonded joints. Protecting gases, such as argon, helium, or a blend of both, are frequently made use of to safeguard the weld pool from responding with elements in the air like oxygen and nitrogen. When these responsive elements enter into contact with the warm weld swimming pool, they can cause porosity, bring about weak welds with reduced mechanical homes.

Insufficient protecting can lead to numerous flaws like porosity, spatter, and oxidation, endangering the architectural integrity of the bonded joint. Sticking to appropriate protecting techniques is important to generate high-quality welds with very little defects and make sure the long life and integrity of the bonded parts.
Tracking and Control Techniques
Just how can welders properly monitor and regulate the welding process to make certain ideal results and prevent defects like porosity? By constantly checking these variables, welders can determine discrepancies from the suitable problems and make prompt modifications to protect against porosity formation.

Furthermore, executing appropriate training programs for welders is crucial for keeping track of and controlling the welding procedure effectively. What is Porosity. Educating welders on the relevance of preserving regular criteria, such as correct gas protecting and travel rate, can aid protect against porosity concerns. Normal assessments and qualifications can additionally ensure that welders excel in tracking and regulating welding procedures
In addition, using automated welding systems can enhance tracking and control capacities. These systems can exactly manage welding criteria, minimizing the probability of human error and guaranteeing consistent weld high quality. By incorporating sophisticated tracking technologies, training programs, and automated systems, welders can efficiently keep an eye on and manage the welding procedure to lessen porosity problems and achieve top quality welds.
Conclusion

Report this page